Alluvial Soil











Alluvial Soil
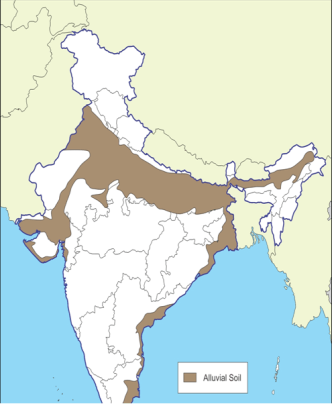
Alluvial Soil: This is the most widespread soil in India, which has been deposited by three important Himalayan river systems - the Indus, the Ganges and the Brahmaputra, covering about 45.6 per cent of the area. Due to its high fertility, areas having this soil are intensively cultivated and densely populated.
Some features of alluvial soil are given below:
Map of India which shows the Alluvial Soil is :
__________________ is the soil of the northern plains of found in Northern India. | |||
| Right Option : A | |||
| View Explanation | |||
Which of the following are correct in context with alluvial soil: (a) This is a rich and fertile soil formed by the deposition action of rivers. (b) Rivers eroded material on their higher reaches and deposit it on their banks they reach the plains. (c) This fertile soil does not supports cultivation of crops. | |||
| Right Option : A | |||
| View Explanation | |||
Which of the following statement(s) is correct about alluvial soil ? 1. It is the most widespread soil in India. 2. It is known for the cultivation of wheat only. | |||
| Right Option : C | |||
| View Explanation | |||
Students / Parents Reviews [10]
My experience was very good with Abhyas academy. I am studying here from 6th class and I am satisfied by its results in my life. I improved a lot here ahead of school syllabus.

Ayan Ghosh
8thOne of the best institutes to develope a child interest in studies.Provides SST and English knowledge also unlike other institutes. Teachers are co operative and friendly online tests andPPT develope practical knowledge also.

Aman Kumar Shrivastava
10thIt has a great methodology. Students here can get analysis to their test quickly.We can learn easily through PPTs and the testing methods are good. We know that where we have to practice

Barkha Arora
10thIt was good as the experience because as we had come here we had been improved in a such envirnment created here.Extra is taught which is beneficial for future.

Eshan Arora
8thI have spent a wonderful time in Abhyas academy. It has made my reasoning more apt, English more stronger and Maths an interesting subject for me. It has given me a habbit of self studying

Yatharthi Sharma
10thAbout Abhyas metholodology the teachers are very nice and hardworking toward students.The Centre Head Mrs Anu Sethi is also a brilliant teacher.Abhyas has taught me how to overcome problems and has always taken my doubts and suppoeted me.

Shreya Shrivastava
8thA marvelous experience with Abhyas. I am glad to share that my ward has achieved more than enough at the Ambala ABHYAS centre. Years have passed on and more and more he has gained. May the centre flourish and develop day by day by the grace of God.

Archit Segal
7thIt was a good experience with Abhyas Academy. I even faced problems in starting but slowly and steadily overcomed. Especially reasoning classes helped me a lot.

Cheshta
10thBeing a parent, I saw my daughter improvement in her studies by seeing a good result in all day to day compititive exam TMO, NSO, IEO etc and as well as studies. I have got a fruitful result from my daughter.

Prisha Gupta
8thAbhyas Methodology is very good. It is based on according to student and each child manages accordingly to its properly. Methodology has improved the abilities of students to shine them in future.
